
- Computer Architecture
- CPU
- Computer Data Storage (Memory)
- Peripheral (I/O)
- Computer Buses
- Chipset - Motherboard
- Expansion Cards
- Embedded System
- Sensor
- Actuator
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
Computer Architecture
Set of rules and methods that describe the functionality, organization, and implementation of computer systems.
Instruction Set Architecture, or ISA. The ISA defines the machine code that a processor reads and acts upon as well as the word size, memory address modes, processor registers, and data type.
Microarchitecture, or computer organization describes how a particular processor will implement the ISA. The size of a computer's CPU cache for instance, is an issue that generally has nothing to do with the ISA.
System Design includes all of the other hardware components within a computing system. These include:
- Data processing other than the CPU, such as direct memory access (DMA)
- Other issues such as virtualization, multiprocessing, and software features.
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
CPU
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
Memory
Memory hierarchy: fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but larger and cheaper options farther away.
Volatility:
- Non-Volatile Memory
- Volatile Memory:
>SRAM
Media:
Semiconductor
Magnetic
Optical
Polymer
DNA
Holographic
Phase Change
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
Buses
| General | |
|---|---|
| Standards |
|
| Storage | |
| Peripheral | |
| Audio | |
| Portable | |
| Embedded | |
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
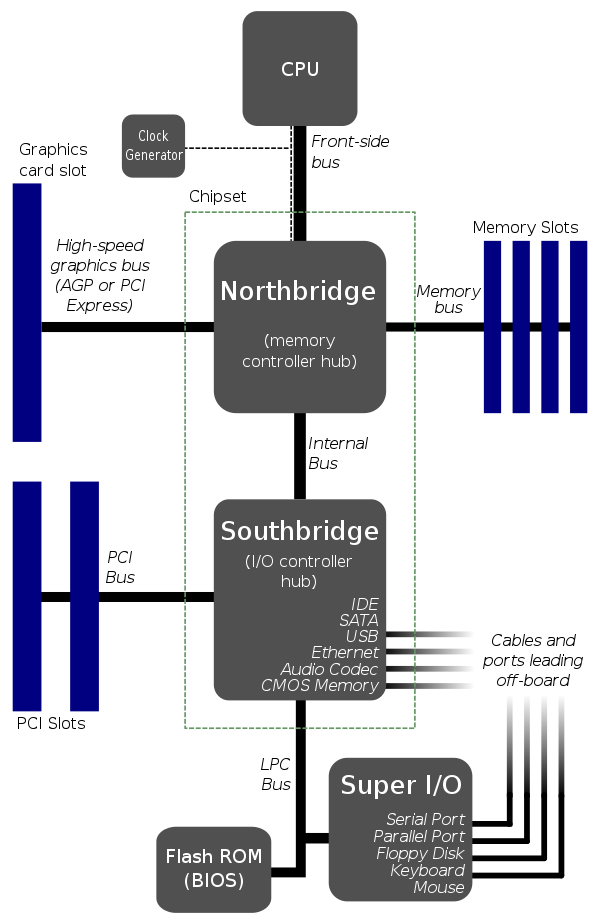
Motherboard & Chipset
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
Embedded System
- do some specific task, rather than be a general-purpose computer for multiple tasks
- Embedded processors can be broken into two broad categories. Ordinary microprocessors (μP) use separate integrated circuits for memory and peripherals. Microcontrollers (μC) have on-chip peripherals, thus reducing power consumption, size and cost.
Applications
Telecommunications: telephone switches for the network to cell phones at the end user. Computer networking uses dedicated routers and network bridges to route data.
Consumer electronics include MP3 players, mobile phones, videogame consoles, digital cameras, GPS receivers, and printers. Household appliances, such as microwave ovens, washing machines and dishwashers, include embedded systems to provide flexibility, efficiency and features. Advanced HVAC systems use networked thermostats to more accurately and efficiently control temperature that can change by time of day and season. Home automation uses wired- and wireless-networking that can be used to control lights, climate, security, audio/visual, surveillance, etc., all of which use embedded devices for sensing and controlling.
Transportation systems from flight to automobiles increasingly use embedded systems. New airplanes contain advanced avionics such as inertial guidance systems and GPS receivers that also have considerable safety requirements. Various electric motors — brushless DC motors, induction motors and DC motors — use electric/electronic motor controllers. Automobiles, electric vehicles, and hybrid vehicles increasingly use embedded systems to maximize efficiency and reduce pollution. Other automotive safety systems include anti-lock braking system (ABS), Electronic Stability Control(ESC/ESP), traction control (TCS) and automatic four-wheel drive.
Medical equipment uses embedded systems for vital signs monitoring, electronic stethoscopes for amplifying sounds, and various medical imaging (PET, SPECT, CT, and MRI) for non-invasive internal inspections. Embedded systems within medical equipment are often powered by industrial computers.[9]
Peripheral
A close-up of the SMSC LAN91C110 (SMSC 91x) chip, an embedded Ethernet chip
Embedded systems talk with the outside world via peripherals, such as:
- Serial Communication Interfaces (SCI): RS-232, RS-422, RS-485, etc.
- Synchronous Serial Communication Interface: I2C, SPI, SSC and ESSI (Enhanced Synchronous Serial Interface)
- Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- Multi Media Cards (SD cards, Compact Flash, etc.)
- Networks: Ethernet, LonWorks, etc.
- Fieldbuses: CAN-Bus, LIN-Bus, PROFIBUS, etc.
- Timers: PLL(s), Capture/Compare and Time Processing Units
- Discrete IO: aka General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- Analog to Digital/Digital to Analog (ADC/DAC)
- Debugging: JTAG, ISP, ICSP, BDM Port, BITP, and DB9 ports.
| General terms | |
|---|---|
| Firmware and controls | |
| Software libraries | |
| Development tools | |
| Operating systems | |
| Programming languages | |
| Microcomputer, personal computer |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midrange | |||||||||||||||
| Large | |||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
Transducer
- Electromagnetic:
- Antennae – converts propagating electromagnetic waves to and from conducted electrical signals
- magnetic cartridges – converts relative physical motion to and from electrical signals
- Tape head, disk read-and-write heads – converts magnetic fields on a magnetic medium to and from electrical signals
- Hall effect sensors – converts a magnetic field level into an electrical signal
- Electrochemical:
- Electromechanical (electromechanical output devices are generically called actuators):
- Accelerometers
- Air flow sensors
- Electroactive polymers
- Rotary motors, linear motors
- Galvanometers
- Linear variable differential transformers or rotary variably differential transformers
- Load cells – converts force to mV/V electrical signal using strain gauges
- Microelectromechanical systems
- Potentiometers (when used for measuring position)
- Pressure sensors
- String potentiometers
- Tactile sensors
- Vibration powered generators
- Electroacoustic:
- Loudspeakers, earphones – converts electrical signals into sound (amplified signal → magnetic field → motion → air pressure)
- Microphones – converts sound into an electrical signal (air pressure → motion of conductor/coil → magnetic field → electrical signal)[2]
- Pickup (music technology) – converts motion of metal strings into an electrical signal (magnetism → electrical signal)
- Tactile transducers – converts electrical signal into vibration ( electrical signal → vibration)
- Piezoelectric crystals – converts deformations of solid-state crystals (vibrations) to and from electrical signals
- Geophones – converts a ground movement (displacement) into voltage (vibrations → motion of conductor/coil → magnetic field → signal)
- Gramophone pickups – (air pressure → motion → magnetic field → electrical signal)
- Hydrophones – converts changes in water pressure into an electrical signal
- Sonar transponders (water pressure → motion of conductor/coil → magnetic field → electrical signal)
- Ultrasonic transceivers, transmitting ultrasound (transduced from electricity) as well as receiving it after sound reflection from target objects, availing for imaging of those objects.
- Electro-optical (Photoelectric):
- Fluorescent lamps – converts electrical power into incoherent light
- Incandescent lamps – converts electrical power into incoherent light
- Light-emitting diodes – converts electrical power into incoherent light
- Laser diodes – converts electrical power into coherent light
- Photodiodes, photoresistors, phototransistors, photomultipliers – converts changing light levels into electrical signals
- Photodetector or photoresistor or light dependent resistor (LDR) – converts changes in light levels into changes in electrical resistance
- Cathode-ray tubes (CRT) – converts electrical signals into visual signals
- Electrostatic:
- Thermoelectric:
- Resistance temperature detectors (RTD) – converts temperature into an electrical resistance signal
- Thermocouples – converts relative temperatures of metallic junctions to electrical voltage
- Thermistors (includes PTC resistor and NTC resistor)
- Radioacoustic:
- Geiger-Müller tubes – converts incident ionizing radiation to an electrical impulse signal
- Radio receivers converts electromagnetic transmissions to electrical signals.
- Radio transmitters converts electrical signals to electromagnetic transmissions.
/------------------------------------------------------------------/
